Research Support at UCLA
Find Subject Librarians to refer students to for help.
There are also research guides that provide general information about finding library resources as well as course specific guides prepared at the request of an instructor.
Finding articles and dissertations
This quick introduction to searching for academic journal articles in databases will help you make your searches more efficient and more effective:
Where to search for articles:
-
Academic Search Complete This link opens in a new windowA multidisciplinary database that indexes over 10,000 publications, with the complete text of over 5,500 periodicals, including a mix of peer-reviewed journals, magazines, and newspapers.
-
Chronicle of Higher Education This link opens in a new window
Full text news and opinion articles covering higher education (2015 - present).
-
Education Source (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window
Includes more than 2,850 education journals, 550 books, and education-related conference papers.
-
ERIC (EBSCO) This link opens in a new window
Index to journal articles and gray literature on educational research and practice from 1969 to the present and ERIC documents since 1966.
-
APA PsycInfo This link opens in a new windowAbstracts and citations to journal articles, books, book chapters, conference proceedings, and dissertations relevant to students, researchers, and professionals working in the psychological, social, behavioral, and health sciences.
-
Web of Science This link opens in a new window
A multidisciplinary database, with searchable author abstracts, covering the journal literature of most disciplines. Indexes major journals with all cited references captured. Combines the following citation databases: Science Citation Index Expanded; Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI); Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI); Conference Proceedings Citation Index.
Tips for finding review articles
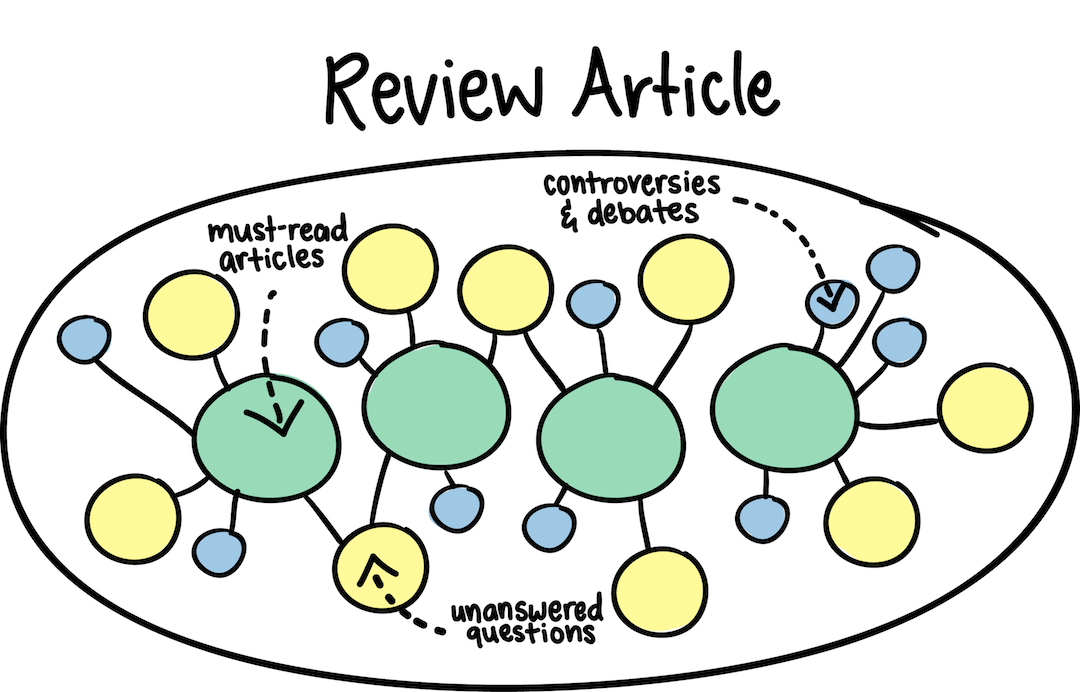
Looking for an efficient way to get a research overview on a topic? A review article is a great place to start.
A review article provides an analysis of the state of research on a set of related research questions. Review articles often: summarize key research findings, reference must-read articles, describe current areas of agreement as well as controversies and debates, point out gaps in knowledge and unanswered questions, suggest directions for future research.
Check out this quick overview of finding review articles in Web of Science, PubMed, Google Scholar, and more.
Finding dissertations
Searching for dissertations is an excellent way to investigate the latest research in a field. Dissertations also often include a literature review and an extensive bibliography, helping you find key sources related to ongoing research conversations.
-
ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global This link opens in a new windowIndex to doctoral dissertations from 1637 to the present, with abstracts since 1980. A number of master's theses are also indexed, with abstracts since 1988. Many are available for download in pdf format. UCLA has access to all full text dissertations in the database. Non-UCLA users may use Dissertations Express to purchase digital or print copies of individual dissertations.
-
WorldCat Dissertations and Theses This link opens in a new windowOver 5 million dissertations and theses available in OCLC member libraries. Many theses are available electronically, at no charge, directly from the publishing institution. UCLA students, faculty, and staff can request non-UCLA dissertations via interlibrary loan.
 |
 |
|
1. Why cite?Watch this quick video for an overview of why citation really matters. |
2. Determine your citation style.Check out the submission guidelines or assignment prompt to determine the proper citation style. When in doubt, ask a researcher in the field, the instructor, or a librarian for help. |
3. Use a citation tool.Check out Zotero, Endnote, or Mendeley to keep track of your articles and create citations. You can also use the citation tools in many databases. Check out our guide to citing sources for more information. |
The Library's online subscription resources can always be accessed from computers and wireless networks on campus. However, off-campus access is restricted to current UCLA, students, faculty, and staff who have set up their computer using one of the following methods.
-
UCLA OnLine Proxy ServerA simple browser setting which will automatically divert you to a UCLA logon page when you first access a restricted site.
-
Virtual Private Networking (VPN)A program you can download and install, or use the built-in version on many computers or mobile devices. VPN software must be logged on manually before you access a restricted site, but works for all programs on your computer.